funções comutativas com sequências infinitesimais.
P = progression.
X √ * / p [n] → log w / w [n] → [p / p P [n]→0
1/ X √ * / p [n] → 1/ log w / w [n] → 1/ [p / p P [n]→0
0.1/ X √ * / p [n] → 0.1/ log w / w [n] → 0.1/ [p / p P [n]→0 [n]
Algebraic logic graceli relativist.
segunda-feira, 14 de setembro de 2015
Aberto do Graceli theory circle. [Differential geometry].
Onde pi be passa um crescente or number with increasing distance between you Pontos de fechamento do circle, ou seja to do circle opening.
P p
r / r * p / p pp = pi / pp / t.
Ou seja, um pi variável and differential number under opening do circle becomes.
Imagine uma broken pulseira that both sides forming puxa um uma opening. E that as this opening tem um ponto da opening decrescente tied or em outro end terminating zero.
E which vary prune opening relação ao tempo em t.
Buy deste prism of criança Imagine um brinquedo opens as uma cool, and this opening will crescente according t o tempo.
Ou seja, vestments spiral com uma side opening, more longitudinal não. Onde são mutáveis as geometric shapes and pi também mutável and variável ao tempo em relação becomes.
Bem com is opening next prune form um tube. E com uma curvature Abertos anéis we will prune form curve variável com uma em relação angle ao tempo.
p P
r / r * p / p /pp = pi / p/p / t. [Â c / t] em relação bend angle ao tempo.
Two anéis uma thread form is prune, prune and two anéis will form um tube. E um longitudinal index is tiver crescimento is prune um cone form.
p p
r / r * p / p pp = pi / pp / t. [AC side / t] [longitudinal / T AC].
Teoria Graceli do
círculo aberto. [geometria diferencial].
Onde pi passa a ser
um numero crescente conforme aumenta o a distancia entre os pontos de
fechamento do circulo, ou seja, a abertura do circulo.
r/ r * p/pP = pi
p/pP /t.
Ou seja, pi se torna
um numero variável e diferencial conforme a abertura do circulo.
Imagine uma pulseira
quebrada que se puxa um dos lados formando uma abertura. E que conforme esta
abertura se tem um ponto decrescente da abertura até o outro extremo que
termina em zero.
E que a abertura
pode variar em relação ao tempo t.
Vendo deste prisma
imagine um brinquedo de criança se abre conforme uma mola, e esta abertura será
crescente conforme o tempo t.
Ou seja, temos uma
espiral com abertura lateral, mas não longitudinal. Onde as formas geométricas
são mutáveis e pi se torna também mutável e variável em relação ao tempo.
Com a abertura bem
próxima se pode formar um tubo. E com uma curvatura nos anéis abertos se pode
formar uma curva variável com ângulo a em relação ao tempo.
r/ r * p/pP = pi
p/pP /t. , [â c / t ] ângulo de curvatura em relação ao tempo.
Dos anéis se pode
formar uma rosca, e dos anéis se pode formar um tubo. E se tiver um índice de
crescimento longitudinal se pode formar um cone.
r/ r * p/pP = pi
p/pP /t. , [âc lateral / t ] [âc longitudinal /t ].
Aberto do Graceli theory circle. [Differential geometry].
Onde pi be passa um crescente or number with increasing distance between you Pontos de fechamento do circle, ou seja to do circle opening.
r / r * p / p pp = pi / pp / t.
Ou seja, um pi variável and differential number under opening do circle becomes.
Imagine uma broken pulseira that both sides forming puxa um uma opening. E that as this opening tem um ponto da opening decrescente tied or em outro end terminating zero.
E which vary prune opening relação ao tempo em t.
Buy deste prism of criança Imagine um brinquedo opens as uma cool, and this opening will crescente according t o tempo.
Ou seja, vestments spiral com uma side opening, more longitudinal não. Onde são mutáveis as geometric shapes and pi também mutável and variável ao tempo em relação becomes.
Bem com is opening next prune form um tube. E com uma curvature Abertos anéis we
will prune form curve variável com uma em relação angle ao tempo.
P P
r / r * p / p/ pp = pi / p/p / t. [AC side / t] [longitudinal / T AC].
P P
r / r * p / p/ pp = pi / p/p / t. [AC side / t] [longitudinal / T AC].
em relação bend angle ao tempo.
Two anéis uma thread form is prune, prune and two anéis will form um tube. E um longitudinal index is tiver crescimento is prune um cone form.
P P
r / r * p / p/ pp = pi / p/p / t. [AC side / t] [longitudinal / T AC].
Teoria algébrica Graceli das impossibilidades por divisões e
elementos sequenciais.
A possibilidade de
haver resutados na função p [progressão], na função r [raiz], na função l [logaritmo].
Numa função
infinitésima seqüencial.
Ou seja, o resultado
nunca é único e sempre se tem sequencias até s.
[F s r+ p + l ],
onde se forma um bloco de resultados para funções
Onde cada função
terá os seus resultados e uma função multiplicado ou somada a outra nunca é 1.
[comutativa transcendente].
E que a função [fs = r + p + i] nunca é 1. E nunca é 0.
E que não se tem um
domínio de uma sequência de uma função dentro de outra. Sendo qualquer for o
infinitésimo.
Homologia para infinitesimais de expoentes
p/pP p/pP +p/pP
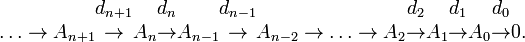
domingo, 13 de setembro de 2015
Algebraic logic graceli relativist.
Where the result can be exact, partial, full, differential, sequential, infinitesimal.
Partial and accurate to the sequential graceli limit [lgs].
Logx / x [n]
1/3
p / p P [n]
1/3 + w to y sequence boundary.
Statistical averaging initial parts, median, final or complete functions ..
Where the results are repeated sequences of numbers and or growing.
Or infinitesimal and relativist. Where is endless and becomes another relativity in the function itself.
Logx / x [n]
1/3 [no limit].
p / p P [n]
1/3 + p [no limit].
For example partial or whole to limit the sequence s.
ςλ p ¨ fx λs.
Σ sum of p λ limit function x to limit the sequence s ς.
for statistical quantity is divided by the sequence until the desired limit.
In other words, here we are decreasing progressive sequential differential, integral partial limit and also algebraic logic to statistics.
The same goes for geometries with progressions as the spiral of graceli, the hat is formed by spirals, moving springs and the snake moving.
Temporal and dimensional geometry graceli.
The infinitesimal of graceli is a descending sequence. Ie they are not only points, but these points have distances and with well defined by the following equations of graceli logic.
I gave this name to algebraic logic to be different from the calculation using integral and differential ,. For use in this case progressions, exponents, roots and logarithms.
double exponent.
Logx / x [n] / Logx / x [n]
1/3 =
p / p P [n]
1/3 + w
Algebraic logic graceli relativist.
Where the result can be exact, partial, full, differential, sequential, infinitesimal.
Partial and accurate to the sequential graceli limit [lgs].
Logx / x [n]
1/3
p / p P [n]
1/3 + w to y sequence boundary.
Statistical averaging initial parts, median, final or complete functions ..
Where the results are repeated sequences of numbers and or growing.
Or infinitesimal and relativist. Where is endless and becomes another relativity in the function itself.
Logx / x [n]
1/3 [no limit].
p / p P [n]
1/3 + p [no limit].
For example partial or whole to limit the sequence s.
ςλ p ¨ fx λs.
Σ sum of p λ limit function x to limit the sequence s ς.
for statistical quantity is divided by the sequence until the desired limit.
In other words, here we are decreasing progressive sequential differential, integral partial limit and also algebraic logic to statistics.
The same goes for geometries with progressions as the spiral of graceli, the hat is formed by spirals, moving springs and the snake moving.
Temporal and dimensional geometry graceli.
The infinitesimal of graceli is a descending sequence. Ie they are not only points, but these points have distances and with well defined by the following equations of graceli logic.
I gave this name to algebraic logic to be different from the calculation using integral and differential ,. For use in this case progressions, exponents, roots and logarithms.
double exponent.
Logx / x [n] / Logx / x [n]
1/3 =
p / p P [n]
1/3 + w
Theory graceli light.
The light undergoes action of magnetic fields and radiation suffering deceleration and deformation. And the light varies in type and density.
The laser has a type and can be stationary within liquid and leave for cracks in other lower plane than entered or higher. And other types of plasmas to have other rates and intensities.
The same applies to radiation and radioactivity of uranium and thorium.
Theory of transcendental numbers.
Every result of the function x, y will be incorporated into the function that will result w, so the procedure continues infinitely.
Log x / x [n].
1 / p / [p / p P] [n].
Transcendent geometry values of transcendental numbers.
Where x is a distance, an angle, or a geometric deformation that will produce other strains, and can also be compared to the intensity values over time.
Imaginative geometry.
Which is neither Euclidean nor curve.
These are images that change as intensity values, movements, time and positions and observers offsets.
Example.
1 / p r / [p r / p P] [n]. [i, m, speed, t, [p, d [observer].
R = radius, or angle, p = progression.
For example geo-algebra by headquarters functions.
Here the functions we do not have numbers, but results of functions sequences or partial results until w limit, or average statistics to ML limit.
1 / p / [p / p P] [n]. {*] X / p / [p / p P] [n]. {*] W / w / [p / p P] [n].
Log xr / xr [n]. {*] Log x / x [n]. {*] Log x / x [n].
Where the result can be obtained by diagonal, or vertical relationship or horizontal.
Geometry spacetime wave speed.
Imagine a tape that is pulled in a wave radiation system often flows x, i intensity.
Thus, this tape will have an angular variation of x wave flows.
Tape speed / wave flow / time. So we have a mathematical and physical reality to a gravitational system, and light in a radiation system.
Where the medium deforms agents and produce another reality.
That is, even if gravity does not become waves to be in a radiation system. And radiation becomes waves. The same eat light and gravity in a radiation system.
Light, gravity = Tape speed / wave / time flow.
And we have a system of a continuum between radiation waves flow, gravity, light, space weather and waves. And radiation.
Sequential progressive analytics.
Function range-graceli.
[P / γ]
1/3 =
Sequence of equal and increasing numbers.
Since γ = p.
P = progression.
Mathematics graceli.
Transcendent mathematics.
When the elements involve more than one result of a function, when they involve more than one branch of mathematics such as algebra, geometry, polynomial, exponents and progressions, and other matrices and statistics. [see theory unified mathematics graceli.
And when it involves results of functions that jump to other functions and become part of them. As the sigma function and gamma- graceli.
Symmetric geometry.
When calculating one side and the results become part of the other side, or the front and smaller in size or larger. Flowers, and members and wings represent it.
Homofórmica geometry.
Where everywhere look, but with a few changes. We see this in the spiral [see hat graceli [published on the Internet].
Infinitesimal for infinitesimal variations on variations.
Infinitesimal variables at x limit the equation passing other stick increasing or decreasing progressive variables.
This can be seen on a horse shooting and tends to reduce its acceleration. That is, within a system infinitesimal infinitesimal have other systems.
Or even a wave having a flow rate and x is replaced by x variables in these flows unstable.
LSG = graceli sequences limit.
Log y / y '[n] to limit [LSG] [a, q, r, p / p P [n], 0]].
a = alternância.
This can be used in geometry, in the calculation, the headquarters, statistics, algebra and theory of sub-infinitesimal numbers.
In this sense we see that employs exponent functions and fractions of these functions. And where you have large numbers when you add or multiply the results of these sequences of sequential functions.
That is, if you have a partial system, infinitesimal and large numbers with the multiplication and even division.
Which can be:
Log y / y '[n] to limit [LSG] [a, q, r, p / p P [n], 0]] / γ.
That is found by a statistical average, or even a matrix system where the results may be different.
That is, if can have varying results, infinitesimal and also great for divisions. Or even have results in ways that are not for addition and multiplication.
So graceli developed another system for calculating it is not by derivatives, differential and integral.
But, for exponents, roots, irrational and transcendental numbers and divisions to address and find great numbers.
In this role you may have limits to the sequence [LSG x], or even have a mean variability involving up to the limit x, or even arrays with crossed sequences results to the x limit, or until the limit x W limit.
And where in this case the symbol leaves the scene, which will serve to other infinitesimal in the same position, or results of infinitesimal numbers to large.
The infinitesimal graceli are not continuous but progressive decreasing sequences and transcendent. You see this in the number of graceli to find the value of pi.
Or the sigma graceli and gamma functions.
* √P X [n] [+, -, / *] log w / w [n] [+, -, /, *] [p / p P [n]
U
P = progression.
X √ * / p [n] [+, -, / *] log w / w [n] [+, -, /, *] [p / p P [n]
U / γ.
Here we have a system that involves root, logarithms and exponents progressions, which may produce large or infinitesimal numbers.
Teoria Graceli da luz.
A luz sofre ação de campos magnético e de radiações sofrendo desacelerações e deformações. E a luz varia de tipo e densidade.
A do laser se tem um tipo e que pode ficar estacionária dentro de líquidos e sair por fendas em outro plano mais baixo do que entrou, ou mais alto. E outros tipos de plasmas se têm outro tipo de velocidades e intensidades.
O mesmo acontece com as radiações e a radioatividade de urânio e tório.
Teoria dos números transcendentes.
Todo resultado da função x, será incorporado à função y que terá o resultado w, assim, o procedimento continua infinitamente.
Log x/ x [n].
1/p /[ p /pP] [n].
Geometria transcendente com valores do números transcendentes.
Onde x pode ser um raio, um ângulo, ou uma deformação geométrica que vai produzir outras deformações, e também pode ser em relação a valores de intensidade em relação ao tempo.
Geometria imaginativa.
Que não é nem euclidiana e nem curva.
São imagens que mudam conforme valores de intensidade, movimentos, tempo e posições e deslocamentos de observadores.
Exemplo.
1 R /p /[ p r /pP] [n]. [i,m,acelera, t, [p, d [observador].
R = raio, ou ângulo, p = progressão.
Exemplo para geo-álgebra por funções de matrizes.
Aqui nas funções não temos números, mas resultados de sequências de funções, ou de resultados parciais até limite w, ou média estatísticas até limite ML .
1/p /[ p /pP] [n]. {*] x/p /[ p /pP] [n]. {*] w/p /[ p /pP] [n].
Log xr/ xr [n]. {*] Log x/ x [n]. {*] Log x/ x [n].
Onde o resultado pode ser obtido por diagonais, ou por relação vertical, ou horizontal.
Geometria espaço tempo velocidade ondular.
Imagine uma fita que é puxada num sistema de radiação de ondas com fluxos de frequência x, de intensidade i.
Logo, esta fita terá uma variação angular de fluxos de ondas x.
Velocidade da fita / fluxo de onda / tempo. Assim temos uma realidade matemática e física para um sistema gravitacional, e de luz num sistema de radiação.
Onde o meio deforma os agentes e produzem outra realidade.
Ou seja, a gravidade mesmo se não for ondas se tornará por estar num sistema de radiação. E radiação se torna ondas. O mesmo acontece coma a luz e com a gravidade num sistema de radiação.
Luz , gravidade = Velocidade da fita / fluxo onda / tempo.
E temos um sistema de um continuum entre radiação fluxos de ondas, gravidade, luz, espaço tempo e ondas. E radiação.
Analítica progressiva sequencial.
Função gama-Graceli.
[ P / γ]
1/ 3 =
Sequencia de números iguais e crescentes.
Sendo γ = p.
P = progressão.
Matemáticas Graceli.
Matemática transcendente.
Quando os elementos envolvem mais de um resultado de uma função, quando envolvem mais de uma ramo da matemática, como álgebra, geometria, polinômio, expoentes e progressões, e outros, matrizes e estatísticas. [ver teoria da matemática unificada Graceli.
E quando envolve resultados de funções que pulam para outras funções e passam a fazer parte das mesmas. Como a função sigma e gama-Graceli.
Geometria simétrica.
Quando se calcula um dos lados e os resultados passam a fazer parte dos outros lados, e ou na frente em tamanho menores e ou maiores. As flores, e os membros e asas representam isto.
Geometria homofórmica.
Onde todos os lados se parecem, mas com poucas alterações. Vemos isto nos espirais [ver chapéu de Graceli [publicado na internet].
Infinitésimos sobre infinitésimos, variações sobre variações.
Infinitésimos variáveis no ponto x do limite as equação que passam ater outras variáveis progressivas crescentes ou decrescentes.
Isto se pode ver num cavalo que dispara e tende a diminuir a sua aceleração. Ou seja, dentro de um sistema de infinitésimos temos outros sistemas de infinitésimos.
Ou mesmo de uma onda que tem um fluxo x de frequência e passa a ter variáveis dentro destes fluxos x instáveis.
LsG = limite de sequências Graceli.
Log y /y ´[n] até limite [LsG] [a, q, r, p/pP [n],0]].
Isto pode ser empregado na geometria, no cálculo, nas matrizes, estatísticas, na álgebra e teoria dos números sub-infinitesimais.
Neste sentido vê-se que se emprega expoente de funções e frações destas funções. E onde se tem os números grandes quando se soma ou multiplica os resultados destas sequências das funções sequenciais.
Ou seja, se tem um sistema parcial, infinitesimal e de números grandes com a multiplicação e até com a divisão.
Que pode ser:
Log y /y ´[n] até limite [LsG] [a, q, r, p/pP [n],0]] / γ.
Ou seja, encontrado por uma média estatística, ou mesmo por um sistema de matriz , onde os resultados podem ser vários.
Ou:
Logx/x [n] Logx/x [n] Logx/x [n] Logx/x [n]
X= p/pP [n] [+,-, * /] p/pP [n] [+,-, * /] p/pP [n] [+,-, * /] p/pP [n] / γ.
Ou seja, se podem ter resultados variados, infinitésimos e também grandes por divisões. Ou mesmo ter resultados por caminhos que não são por somas e multiplicações.
Assim, Graceli desenvolve outro sistema para o cálculo que não é por derivadas , diferenciais e integrais.
Mas sim, por expoentes, raiz, números irracionais e transcendentes, e divisões para resolver e encontrar números grandes.
Logx/x [n] Logx/x [n] Logx/x [n] Logx/x [n]
X= p/pP [n] [+,-, * /] p/pP [n] [+,-, * /] p/pP [n] [+,-, * /] p/pP [n] / γ.
Nesta função se pode ter limites até a sequência [lsG x], ou mesmo ter um variabilidade envolvendo médias até o limite x, ou mesmo de matrizes com resultados cruzados de sequências até o limite x, ou do limite x até o limite w.
E onde neste caso o símbolo sai de cena, que servirá para outros infinitesimais na mesma função, ou para resultados de números dos infinitesimais até os grandes.
Os infinitésimos Graceli não são contínuos, mas sim sequências decrescentes progressivas e transcendentes. Se vê isto no número de Graceli para encontrar o valor de pi.
Ou nas funções sigma e gama Graceli.
X* √p [n] [+,-, / *] log w / w [n] [ + , -, /, *] [p / pP [n]
U
P = progressão.
X* √ /p [n] [+,-, / *] log w / w [n] [ + , -, /, *] [p / pP [n]
U / γ.
Temos aqui um sistema que envolve raiz, logaritmos, e expoentes de progressões, e que podem produzir números grandes ou infinitésimos.
Assinar:
Postagens (Atom)